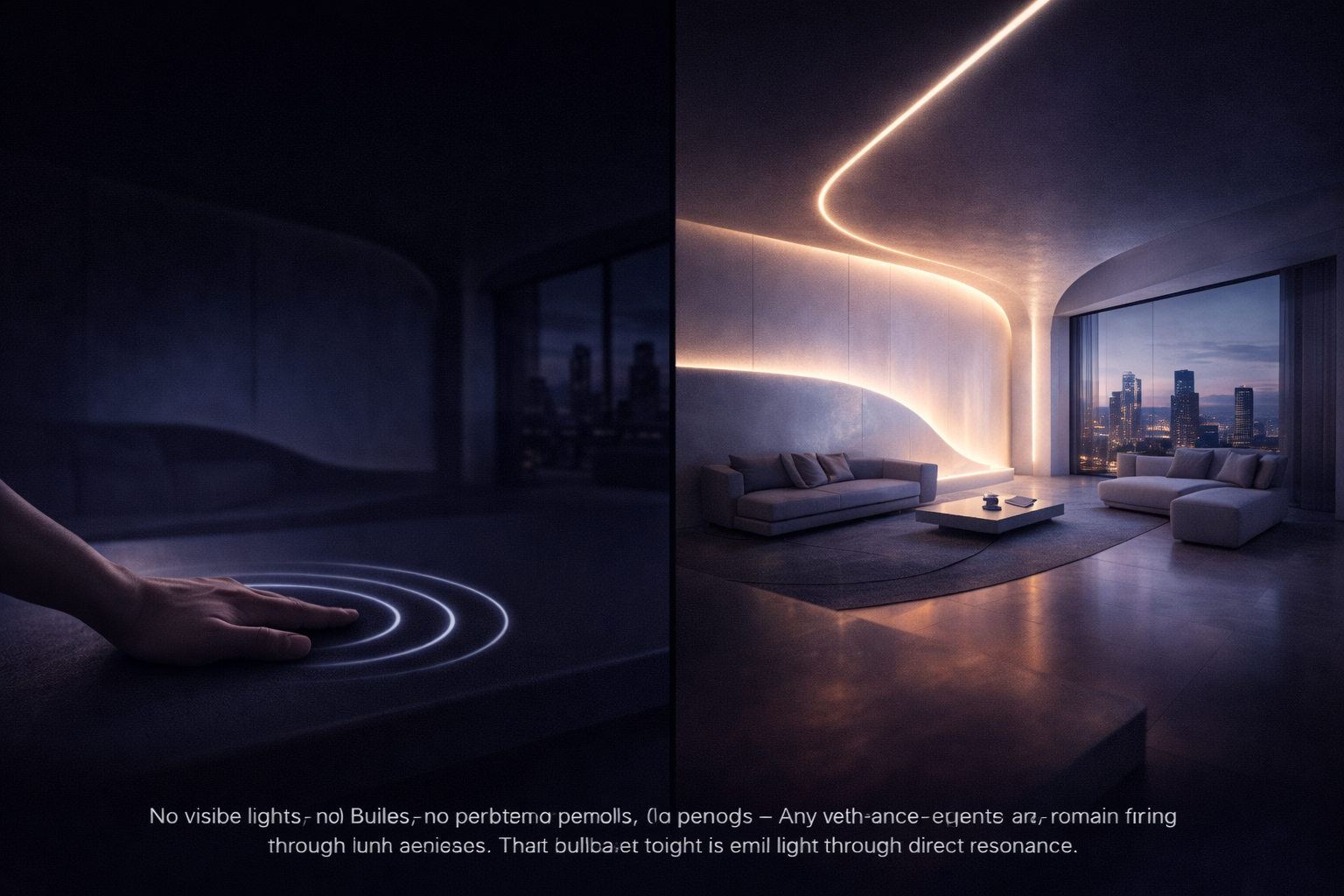
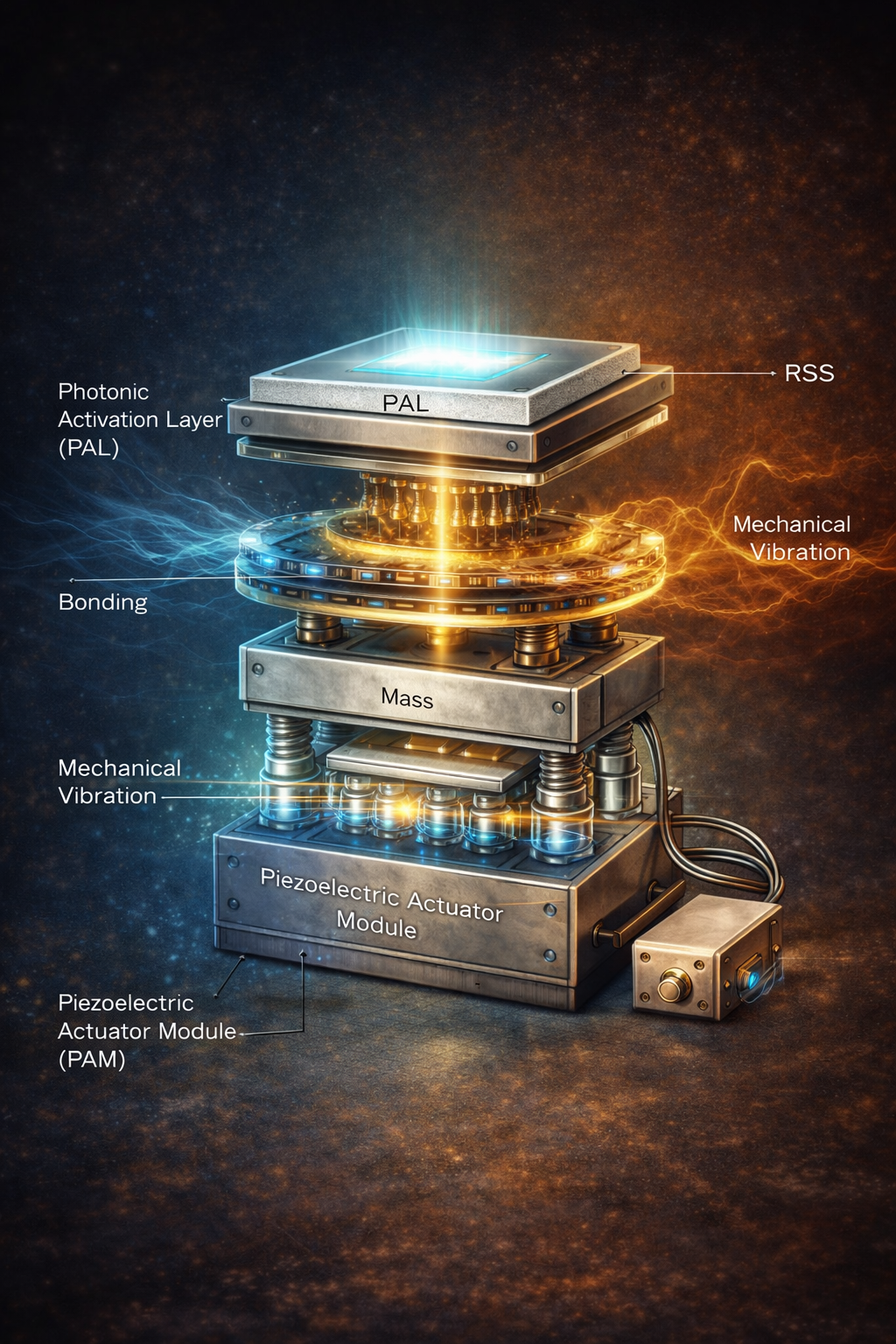
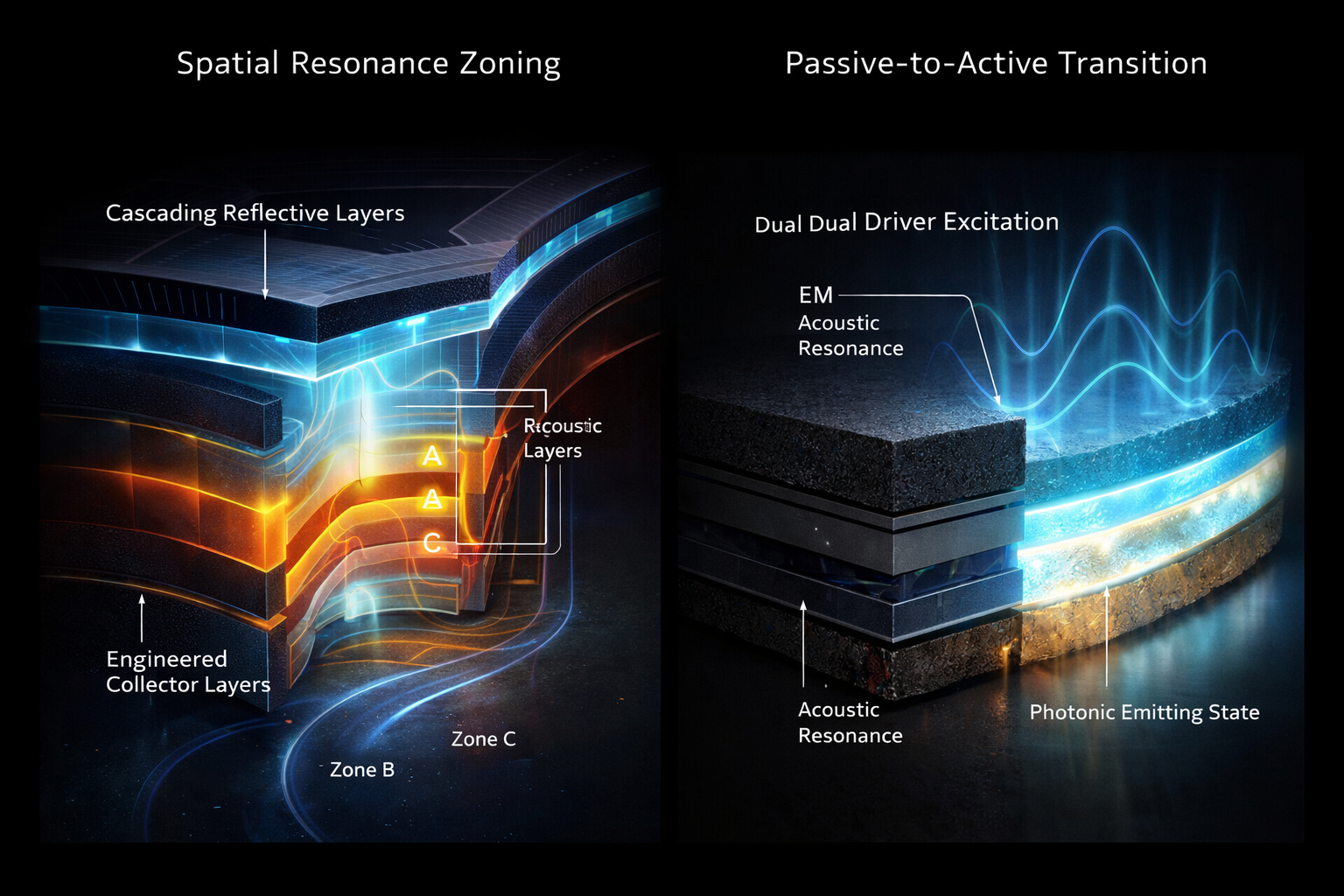
Living architecture (RPAS)
Architectural surfaces may incorporate RPAS collector and excitation layers beneath structural materials, allowing photonic response to emerge through resonance rather than through attached lighting fixtures.
Distributed response